Adding Basic Pages
Pages such as a privacy policy and terms and conditions pages should be included in your website; They indicate to google that you are an authority site while also increasing the trust factor to your viewers.
These pages do not need to be unique and you do not need to spend a lot of time writing this information.
They can be generated using tools such as h-supertools.
Other pages which are useful to include with minimal effort include a contact and about page.
An about page is a good place to provide information to the user about your business or organisation such as its purpose, values, creator/author credentials, as well as any relevant certificates or guarantees.
Custom Error Pages

You must ensure that your sites error pages do not output any specific information such as server side error details that could be a security and user experience concern.
These pages are also a good location to provide users with access to important pages of the site thus increasing the likelihood of retention.
To indicate that pages have been moved or deleted, a 404 error should be returned when the request for the error page is executed. You must not return a ‘soft 404’ which returns a success status code instead of a 404 code.
Redirects
A redirect should be used in formats such as 301 (permanent) or 302 (temporary).
Redirects can indicate to search engines that content has permanently or temporarily moved.
As outlined by Googles Guidelines, meta (client-side) refreshes should be avoided and only HTTP server-side redirects should be used.
Chained redirects are where a page is redirected to further pages with additional redirects. This can cause problems for both user experience and SEO and should be avoided. If you are unsure of current status codes, chromes link redirect trace tool can be used to identify returning status codes currently used in a site.
URL Structure
The URL structure should be thought through thoroughly as it can be difficult and potentially damaging to change.
This is because it can take a while for search engines to recognise the changes and therefore redirects are required. A URL structure change can also be damaging if backlinks have been built for pages that are to be changed.
If a change is required, the valid HTTP forwarding should be applied.
They are used as an identifier of the content and its hierarchical structure. For example, the following URL clearly explains where the t-shirt is located in the sites directory:

Additional parameters in the URL path should be in readable format where possible and should not contain anything that does not alter the pages contents.
It is important to keep the URLs simple and consise and to format them with keywords whereby each word is divided by a hyphen.
So, in summary of URL structure best practices:
- Bare careful if you need to change it
- Setup valid HTTP forwarding if a change is necessary
- Make your path in human readable format where possible
- Divide words with hyphens
- Avoid parameters that do not alter the contents of a page
Site Structure

The site structure is another important aspect of technical SEO from different angles such as site readability, relevance, search engine crawling ease, and user experience.
Another consideration is the search engine results page (SERP) navigational features that can be incorrectly populated if the site structure in invalid. The following image shows Currys’ navigational components in the SERPS, which has been generated based on factors such as site structure, site analytics and internal links.

As well as the sitemap file which will be explained, creating a visual sitemap can help to plan the hierarchical structure of a site and illustrate the connections and order of pages to ensure the correct decision is made.

This can also help to develop content and internal linking ideas.
Some keys tips when creating the site structure include:
- The most important web pages (parent pages) should link to the most relevant and important sub pages (child pages)
- Child pages should link to related child pages and their parent pages.
- It should not be difficult to navigate to any important pages within 2-3 clicks
- The site structure should be translated into the navigation bare with clear ordering and structure. (UL and LI tags should be used for the navigation bar)
- Pages should not be deeper than 4-5 levels. Structure should often be reconsidered if this is the case.
Linking

Building backlinks is a crutial element of SEO.
But it is outside the scope of this guide and is refered to as ‘off-page SEO’.
External and internal linking is, however, a large component of technical SEO.
Contextual and External Linking
External links are hyperlinks that redirect users to external sites/resources.
They are helpful in providing value to users, especially with educational content.
However, it is advised to be cautious of directing users off your site to other services… for obvious reasons.
For any external links that are sponsored, paid or affiliate, use the rel=”sponsored” or rel=”nofollow” atributes for the a tag.
Internal Linking
Internal links are hyperlinks that direct users to other pages on the same domain.
The count of internal links to specific pages is a factor used by Google and other search engines to determine which pages have the highest priority. This can ultimately lead to how your site links are formatted in the search engine.
Because of this, be conscious of linking unimportant pages. For example, a contact us link at the bottom of each page can build up to a high count and degrade other important pages significance.
It is a good idea to keep a count of internal links using Google Search Console or other tools.
Internal links should be formatted inside a tags with HREF attributes and with keyword rich terms used as the anchor text like as follows:
<a href="link">Web Design Services</a>As like all areas on the site, try to primarily use links with anchor text so its content can be used to describe the benefit the link provides to the user.

Breadcrumbs are a no brainer for bigger sites and are a great example how how to emphasise the structure of your site as well as add the vital internal links.
Any broken links can damage your SEO efforts, so, be sure to keep an eye on links used through link checkers such as IPullRank or Screaming Frog.
The internal linking tips can be summarised as follows:
- Keep a count of internal links to organise page priorities
- Use a tags with HREF attributes
- Use keyword rich anchor text
- Consider breadcrumb components
- Analyse and amend broken links
Graphics

Graphics are an important elements of a webpage and can be used to enhance user experience such as to make extensive text more easily readable.
Graphics can come in the format of videos, photos, and designs.
While graphics can be powerful, it must be considered that when there is text inside an image or video, unless its written as HTML over the top of the content, the text will not be used as a ranking factors.
Images
As like page names, image names should be keyword rich and separated with hyphens.
Images should be formatted and compressed to help with optimal page load speed.
Modern formats which should be considered include:
- JPEG 2000
- JPEG XR
- WebP
Different compression types such as lossless and lossy can be beneficial in different cases depending on your individual situation.
Although, the browser compatibility of new technologies should be analysed as fall-back formats may need to be provided.
The resolution of an image can effect how quickly a page loads and how large the image file is.
For example, if a mobile website loads images at 1920×1080 when the display resolution of 480×270, then the page is unnecessarily loading the image at 400% its rendered dimensions.

You can find out the resolution of an image in Google Chrome Console by inspecting the image elements SRC tag with your mouse, and comparing the intrinsic dimensions (real image size) and rendered dimensions (image size on website).
This can help to find out where compression is needed.
The quantity of graphics on a page can also cause slow loading speeds.
If this is an issue, you can investigate lazy loading. Lazy loading can be used to render the image contents when the image content is in the viewport of the user.
Although often effective, I would advise to only use lazy loading as a last resort after other potential reasons have been tested.
In summary:
- Compress images to their rendered image size
- Consider modern image formats such as WEBP, JPEG 2000 or JPEG XR
- Consider lazy loading for image dense pages/sites
Videos
Videos are a rich resource that can provide extra value and appeal to users.
This guide will only cover the embedding or loading of videos on your website and how to optimise for search engines and not how to rank your video on platforms such as YouTube.
Videos can be embedded into your site and uploaded via an external services such as Vimeo or YouTube, or can be loaded from your server.
The following technical points can help optimise the videos on your site:
- Describe your video with the title tag
- Include keywords in the tags of your video
- If you use extensive videos, create a video sitemap
- If applicable, try to increase your user interaction such as likes, comments and shares.
Image Descriptions
<img alt="This is my image description"/>Image alt tags can be used inside image elements to describe the contents of the graphic.
This helps for the search engines to understand how the image relates to the content.
It advised to use the following guidelines when writing image alt tags:
- Make it between 30 and 125 characters
- Include your target keywords
- De descriptive but dont “keyword stuff”
- Make each different image alt unique, unless its only the resolution, dimensions, or size that has changed
<div id="background-image" title="This is my background image description"></div>Try to avoid background images where possible as they are identified as less significant than image elements and the descriptions aren’t used for SEO as much. But, where needed, describe the image in a title attribute.
Titles
<title>Technical SEO - Full Guide (20+ Topics) - CodeVictor</title>The title of a page outlines its content and is a great place to incorporate your target keywords.
You should try and consider the users perspective to develop an appealing title that will attract viewers.
Use the following steps to help with creating titles
- Use title case
- Aim for between 30 and 60 characters
- Use keywords and put most important first where possible
- Avoid using company name at the front apart from non ranking pages such as the home page, use it at the end.
Headings

Headings are a huge aspect of SEO and like titles, help to identify the keywords a page should be ranking for.
Tools can be used to analyse the count of heading tags in a websites pages such as SEOReviewTools.
- Aim for headings between 20 and 70 characters
- There should only be one h1 tag in each page that is aiming to rank on the SERPs.
- The primary keyword(s) should be placed in the heading for emphasis of its relation to the content.
Meta Descriptions

Meta description tags describe the pages contents for search engine results pages.
For services, it is a good place to sell your value and business. For tutorials, it is a good place to invoke educational curiosity.
Although it is essential to write your own meta description, it must be noted that google may replace your description with alternatives they believe will help your rankings. So, do not be alarmed if the meta description you see for your site in the SERPs does not match exactly what you’ve written.
The following guidelines will help you write your meta descriptions:
- Make sure each pages meta description is unique
- Aim for between 60-140
- Avoid double quotes (“) as they are perceiving as an indicator to cut off the following content after it
- Start with primary keywords where possible but make sure it reads well to the user
Content

While the actual creation of content is regarded as on-page SEO, rather than technical, there is technical knowledge that can be applied to this area:
- Use a tags and HREF attributes for links
- Use keyword rich anchor text
- Use strong tags and not b tags for emboldening
Duplicate Content
Duplicate content refers to two or more pages that share the same information/content. This can be damaging for SEO because it can be an indication of Black Hat SEO tactics.
Duplicate content can be in the following forms
- URL variations
- Replica pages
- www and non-www websites
- HTTP and HTTPS website pages
URL Variations
URL variations are pages that contain the same content on a domain with different URLs.
An example includes the two following links:
www.example.com/clothes/t-shirts/lacoste-smallwww.example.com/all-clothes?type=lacoste-smallThe damage to SEO can be eliminated if a link tag is included in each duplicate variation of the same page, pointing to the original page. As follows
<link rel="canonical" href="original-page-link">Replica Pages
Minimal duplicate content within the same domain is not always deemed as harmful. It is common for components such as navigation buttons and footer information to be reused accross the website. This is not a problem.
The problem exists when there is extensive text copied acrross one or more pages. This problem can be resolved by:
- Extensively rewording the content
- Including a canonical tag
- Excluding the page from being indexed using the no-index capabailities in robots.txt
www/non-www and HTTP/HTTPS
Both www/non-www and HTTP/HTTPS duplicate content issues can be resolved by setting up a 301 permanent redirect to either www or non-www prefixed domains and to the HTTPS version of the site.
CSS and JavaScript
Both CSS and JavaScript are often a vital component for websites and web applications but when done incorrectly, can have a negative impact on SEO.
As per standard programming convention, CSS should be included in the head tag and JavaScript should be included before the body closing tag. It is often argued that the JavaScript should also be placed inside the head tag but this can cause problems if it is referencing HTML elements that will not yet have been rendered.
Using external references to online code can be potentially harmful to your sites user experience and security.
This is because:
- If the content you are linking to is moved or altered, it can effect the design and overall user experience of your site.
- If the code that your site is linking to gets hacked, malicious code could get injected and used in your site.
It is not always applicable with one example being when API keys are included as a URL parameter. So, if you cannot move it locally, make a note to keep an eye on it.
Bundling and Minifying
The bundling of JavaScript and CSS can be beneficial for your site because it can collate the logic into one file which can implement HTTP caching to improve your sites performance.
This HTTP caching needs to be setup and can be done so using this guide from Google. It is fairly straight forward and can have a huge effect on return user site speeds.
Minification is also beneficial because it reduces the physical size of your CSS and JavaScript by condensing the logic. This is achieved by removing unimportant space such as whitespace. Therefore, the server passes less data through the HTTP requests which speeds up the response times.
JavaScript
Be wary of dynamic JavaScript in your code. Although less of a concern with Google now executing JavaScript on page render, excessive dynamic JavaScript can shift the pages content and negatively impact the Cumulative Layout Shift and therefore, your ranking.
Avoid infinite scroll plugins. This feature can prevent pages and content from being crawled and therefore ranked.
CSS
Minimise inline styles where possible and try to include all CSS in a separate file to be bundled and minified.
Ensure that the CSS properties used are valid and not depreciated.
Page Load Speeds
Most areas of how to improve your website load speeds has been covered already and will be covered in the following ‘core web vitals’ section. To illiterate, the main steps are:
- Minify and bundle JavaScript and CSS
- Use a capable server
- Compress and optimise images
- Remove unused content
- Consider asynchronous calls for scripts, stylesheets, graphics and content
- Consider lazy loading
- Implement the following core web vitals tips
Core Web Vitals

Core Web Vitals is a metric used by Google from November 2020 as a search ranking factor. It encompasses three main variables which are:
- Largest Contentful Paint
- First Input Delay
- Cumulative Layout Shift
Core Web Vitals can be measured using tools such as PageSpeedInsights, GTMetrix and WebVitalsLibrary.
Largest Contentful Paint
Largest contentful paint refers to the time it takes for your page to load the majority of the content in the viewport. Note that the use of the word viewport is used rather than page.
Viewport means the area of the page that the screen is showing and user is seeing.
Largest contentful paint can be improved by researching and implementing the following practices and principles:
Improving CSS and JavaScript Management
- Use the preconnect or preload attribute for CSS so that the browser can establish a connection to the destination server more quickly
- Minimising CSS and JavaScript
- Bundling CSS and JavaScript and implementing HTTP caching
- Using CDNs instead of local or external sources
- Defer JavaScript and CSS to avoid the webpage having to wait for the resource to fully load
Improving Server Response Time
- Consider new graphic formats such as WEBP and JPEG 2000
- Compress and format images to correct resolution and sizes
- Investigate any potential server issues
- Consider lazy loading
A great resource that can be used to extend your knowledge on the topics covered and to further reduce the largest contentful paint times is this article from web.dev.
First Input Delay
First input delay refers to the time taken for the web page to load interactive elements in a usable state.
The majority of the time, JavaScript intefers with this performance rating. This is because when a web page is rendered, its HTML code is displayed first, followed by the JavaScript. If JavaScript is powering the interaction capabilites, the browser must then wait for the related JavaScript to be fully executed before elements are interactable.
The ideal delay time is below 100ms.
This can be minimised by:
- Ensuring threads aren’t blocked
- Defering relevant JavaScript
- Minimising and bundling relevant JavaScript
- Consider pre-connecting, pre-loading and pre-fetching JavaScript
- Consider lazy loading
- Implement HTTP caching
Cumulative Layout Shift
Cumulative layout shift is explained as a measure of how the content differs when initially displays compared to when fully loaded.
With a poor cumulative layout shift, the content may shift its position and/or dimensions when the page is fully loaded. This could result in poor user experience and could mean that when a user interacts with an element, its action is not executed.
Tips to improve the cumulative layout shift of your site includes:
- Explicitly add height and width values to your images and ad, iframe and embed containers,
- Avoid asynchronous actions if they result in the adjustment of the pages layout
Server
If you are hosting on a shared server, you can run a reverse IP check to find other websites that are sharing your IP. You can then use this information to check if any are blacklisted, which, although is rare, could be potentially damaging your sites rankings.
Security

Using an SSL certificate is imperative in a website these days.
Google Chrome displays a warning screen before a user accesses a site with no SSL which can diminish user trust and experience.
You must setup a permanent redirect for the HTTP version of the site to forward onto the HTTPS version. This is best achieved with a 301 redirect.
Google safe browsing was introduced in 2007 and contains a list of malicious websites. Its contents is used by all major browsers to warn users of dangerous sites.
A transparency report is a great tool to identify any unsafe content or site security issues and whether your site is on this safe browsing blacklist.
Making Sure Search Engines Can Render & Search Your Site
Without making sure that search engines can crawl and render your site, your other SEO efforts are wasted.
XML Sitemap
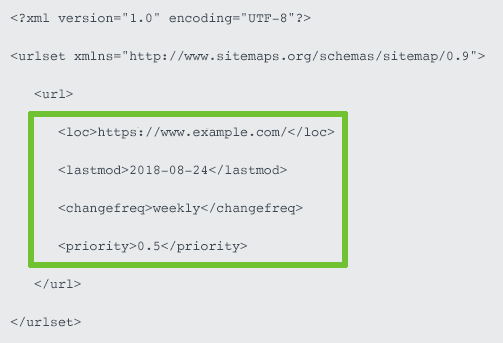
An XML sitemap outlines the URL structure of your site as well as further information about pages such as when it was last updated, its priority and the page relations.
You can generate XML sitemaps with tools such as xml-sitemaps.com. Its information is in XML format and is pretty easy to add to and understand.
Providing you have connected Google Search Console, you can also check which version of your sitemap(s) Google are using to index and crawl. If it is incorrect, you may need to submit the correct version.
If you have a large site, your sitemaps can be divided into separate sitemaps for components such as posts, pages, news, images, and videos.
Robots.txt

A robots.txt file can be used to outline to Google and other search engines which pages do not need.
The user agent value defines which crawling bots the restrictions apply to, with an asterisk (*) meaning all bots.
The disallow and allow values are used to explain to the crawling bots which directories or pages they are allowed or disallowed to crawl. There can be multiple rows of allow and disallow information.
For example, the above logic inside a robots.txt file excludes the bots from crawling any WordPress related pages/data.
Checking Response vs Render
Checking how your website is shown to the search engines compared to how you perceive it might help identify issues with your sites render state vs response state.
This is especially applicable for heavy dynamic JavaScript pages.
Tools such as Site Bulb provide response vs render capabilities that can help you ensure everything you want to be indexed, is being indexed.
Conclusion

I hope this guide has been useful for you. Please take the time to use the information provided to expand your knowledge base. Any areas you wish to implement after reading this guide should be further researched to reinforce your understanding. I recommend blogs such as SEOSLY, Neil Patel, Ahrefs, MOZ, and of course Googles official documentation.
Although many areas of technical SEO have been covered in this tutorial, some further reading includes:
- Structured data/schema
- On page SEO
- Off page SEO
- Link building
- Local SEO
Remember, you cannot achieve technical SEO without any effort. You must take the time to implement all the tips and steps advised in this guide while tailoring it for your specific needs.
Technical SEO is not all that is needed for your search engine efforts. Without on-page and off-page SEO efforts combined into your strategy, You will find it hard achieve success in this field.
Www icons created by Freepik – Flaticon
